Efforts to Reduce Environmental Impact
Fiscal 2001 marks the year in which Kuraray established and initiated its Medium-Term Environmental Plan. Today, the Company continues to promote activities to achieve its specific goals. By implementing the following measures, the Okayama Plant is steadily working to advance the reduction of environmental impact.
1. Global warming efforts
Kuraray's Okayama Plant is exerting energy-saving efforts as a global warming countermeasure that aims to reduce CO2 emissions.
 Note: All figures are crude oil equivalents
Note: All figures are crude oil equivalents
Kuraray is promoting conversion to natural gas at its Okayama Plant in lieu of C heavy oil used as fuel in its power station's heavy-oil-burning boilers. As of January 2006, one of its two boilers had been converted to natural gas use already. Conversion of the remaining boiler is scheduled for January 2007, with efforts to meet this goal under way. Looking ahead, the continued conversion to cleaner fuel sources will greatly contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions.
Kuraray is also working to reduce CO2 emitted from in the transportation and delivery of products through "modal shift (*1)" measures.
- *1 Modal shift
- Using ships and trains for product transportation in place of trucks
2. Chemical waste reduction
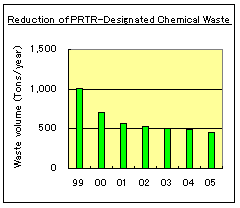
The Okayama Plant is working to reduce its volume of chemical waste, particularly of chemical substances designated by the PRTR Law (*2) and the Japan Chemical Industry Association (JCIA), through capital investment and transitioning to safe chemical substitutes.
The Plant was successful in reducing PRTR-designated chemical substances and substances defined under JCIA's independent chemical management measures by 51% in fiscal 2005 compared with fiscal 1999.
- *2 PRTR Law
- The Pollutant Release and Transfer Register Law promotes improvement in the control and management of chemical substance emission volumes into the environment.
3. Waste reduction
Targeting zero waste emissions, the Okayama Plant is exerting efforts to better control waste generation, recycle and reuse. Kuraray defines zero emissions for the Okayama Plant as follows.
Advancing the effective use of waste products, the Company stipulates that the final volume of waste disposal remain below 1% of the volume of waste generated.
The Okayama Plant met their fiscal 2005 zero emissions target two years ahead of schedule in fiscal 2003.
4. Major environmental countermeasure investments
| 1998 | KURALON K-Ⅱ waste gas incinerator | approx. ¥100 million |
| 2001 | CLARINO waste gas incinerator | approx. ¥300 million |
| 2001 - 2002 | Boiler smoke emission countermeasures (phases 1 & 2) | approx. ¥1 billion |
| 2002 - 2003 | Power plant turbine efficiency measures (phases 1 & 2) | approx. ¥400 million |
| 2003 | Waste heat recovery through the use of hot water circulated during the PVA to KURALON process | approx. ¥100 million |
| 2004 | Waste heat reuse through PVA recovery processing equipment | approx. ¥100 million |
| 2002 - 2006 | PVA process: switched to high efficiency brine refrigerating machine | approx. ¥100 million |
| 2005 | Raised manufacturing efficiency through improved PVA saponification equipment | approx. ¥200 million |
| 2005 - 2006 | Boiler fuel switch to natural gas (phases 1 & 2) | approx. ¥1 billion |
